There are two power inverters: low frequency and I-inverter ephezulu.
Off-grid inverters are straightforward devices that transform the DC power stored in batteries (direct current, 12V, 24V, or 48V) kumandla e-AC, which can be used to run household equipment like refrigerators, televisions, and phone chargers. Since they can easily supply a large amount of electricity, a I-Inverter yeMpumelelo is a need for anyone with no access to the main power source.
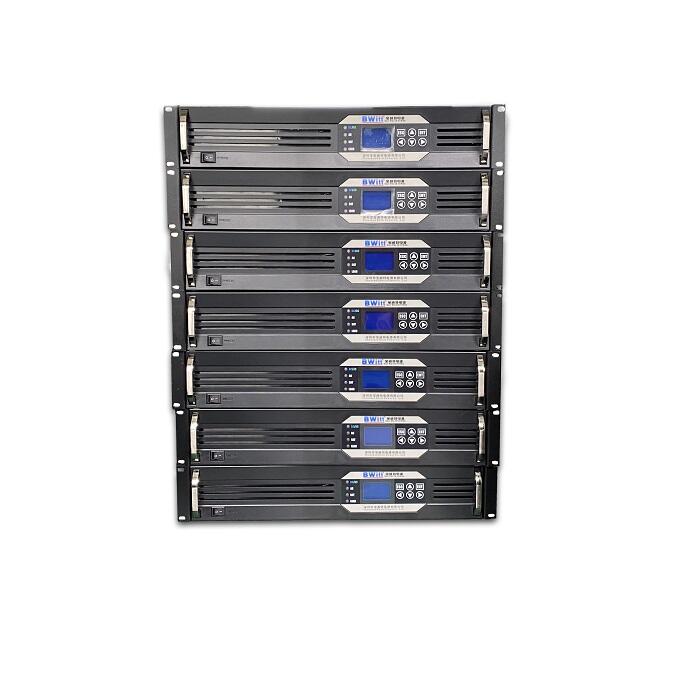

Peak power capacity and dependability are areas where low-frequency inverters excel over high-frequency inverters. Compared to high-frequency inverters, low-frequency inverters are built to handle larger power spikes over a longer period.
High-frequency inverters can run at a 200 percent power level for only a brief period. In comparison, low-frequency inverters can function at a peak power level of up to 300 percent of their nominal power level for several seconds.
The high-frequency inverter uses MOSFETs, which use electronic switching and are more prone to damage, especially at high power levels. On the other hand, low-frequency inverters function using powerful transformers, which are more dependable and durable.
In addition to these characteristics, low-frequency inverters have a vast array of technological features and abilities that most high-frequency inverters do not have.